SNMP Monitoring
SNMP is one of the most commonly-used communications protocols online. Short for “Simple Network Management Protocol,” it belongs to the application layer of the Internet protocol suite, a set of popular online protocols. Other protocols in the application layer include HTTP, FTP, SMTP, and DHCP.
SNMP originated in the 1980s as networks were growing in size and complexity. Today network administrators use SNMP to get performance information about the devices on their network. SNMP monitoring includes getting data from SNMP-enabled devices about their activity, like bytes, errors transmitted and received, or connection speed.
SNMP Monitoring Software Benefits
You need a way to manage all your network devices. It can be overwhelming to try to manage it all, especially if you have a small network team, or if you have a rapidly-growing network.
Monitoring software for SNMP helps capture information about how your SNMP-enabled devices are performing. Most devices speak SNMP, and this could include everything from network equipment and servers to printers and applications.
A monitoring tool can also help with inventory and asset management and security.
Lastly, a reliable SNMP monitoring tool helps anyone reliably monitor large quantities of data from a single console with limited resources—even if you're a one-person IT team. More efficient monitoring can give you peace of mind, knowing you can monitor traffic in real time, identify performance slowdowns, avoid bandwidth and server performance issues, spot trends, and improve the overall health of your network.
Meet Intermapper, Your Go-To for SNMP Monitoring
Intermapper is network monitoring software for Mac, Windows, and Linux that can easily and reliably monitor all your SNMP-enabled devices. Unlike other SNMP-monitoring tools, Intermapper comes with built-in SNMP probes you can use to monitor all kinds of equipment—and you can also build your own.
Along with flexible monitoring for anything with an IP address, here are more reasons IT professionals love Intermapper:
Live visual mapping
Unlimited map personalization
Configurable alerts
Cross-platform compatibility
Network automation
Bandwidth analysis
How Does Intermapper Monitor SNMP?
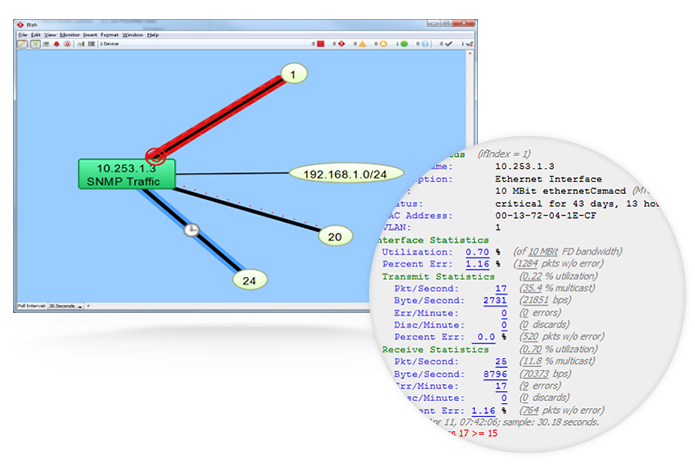
Intermapper uses SNMP probes to query network devices for their management information base (MIB) variables. Those MIBS give you a greater range of SNMP monitoring. Out of the box, Intermapper comes with all kinds of general and vendor-specific probes, including:
- Basic OID
- Comparison
- High, Low, or Range Threshold
- Restricted Interface
- Single OID Viewer
- SNMP High PPS
- SNMP High Traffic
- String Comparison
- Table or Trap Viewer
- And more!
If you need a different SNMP probe, check out our user-contributed probes library. Customers constantly share custom SNMP probes and other types of probes for the whole Intermapper community to use.
You can also create your own custom SNMP probes. Here is a helpful article on how to create an SNMP probe.
Helpful SNMP Monitoring Resources
Three SNMP Versions
There are three versions of SNMP. Here's a quick summary of each version and how they differ:
SNMPv1
SNMPv2c
SNMPv3
Seven SNMP Protocols
There are seven different SNMP protocol types. The four that are most commonly used by network administrators include GetRequest, GetNextRequest, Response, and Trap. Intermapper only requires read-only access to any of the “get” commands.
1. GetRequest
2. SetRequest
3. GetNextRequest
4. GetBulkRequest
5. Response
6. Trap
7. InformRequest
Try SNMP Monitoring Free for 30 Days
Identify performance trends for SNMP-enabled devices and troubleshoot issues faster with Intermapper. Try it free for 30 days.