What is Data Security?
Generally, data security is described as all that surrounds the protection of digital data from destructive forces or unwanted actions of unauthorized users, such as from a cyberattack or data breach. By this overarching definition, the one thing data security is not is a singular software solution that claims to “do it all.” Rather, data security is a mindset and a coordinated, concrete set of efforts and software solutions deployed throughout an organization designed to comprehensively protect the sensitive data transmitted each day at all stages of its journey.
Why Data Security Matters
If your data is vulnerable to cybersecurity thieves, or even to human error, be prepared to pay – financially, with personnel resources, and in rebuilding your reputation should a breach occur from within or outside of your enterprise. According to a study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach is estimated at $3.92 million. Industries that are highly targeted for their valuable personal information like finance, healthcare, and retail can see an even higher toll. No matter your industry, if you store or transfer identifiable, sensitive data, your organization is an attractive target.
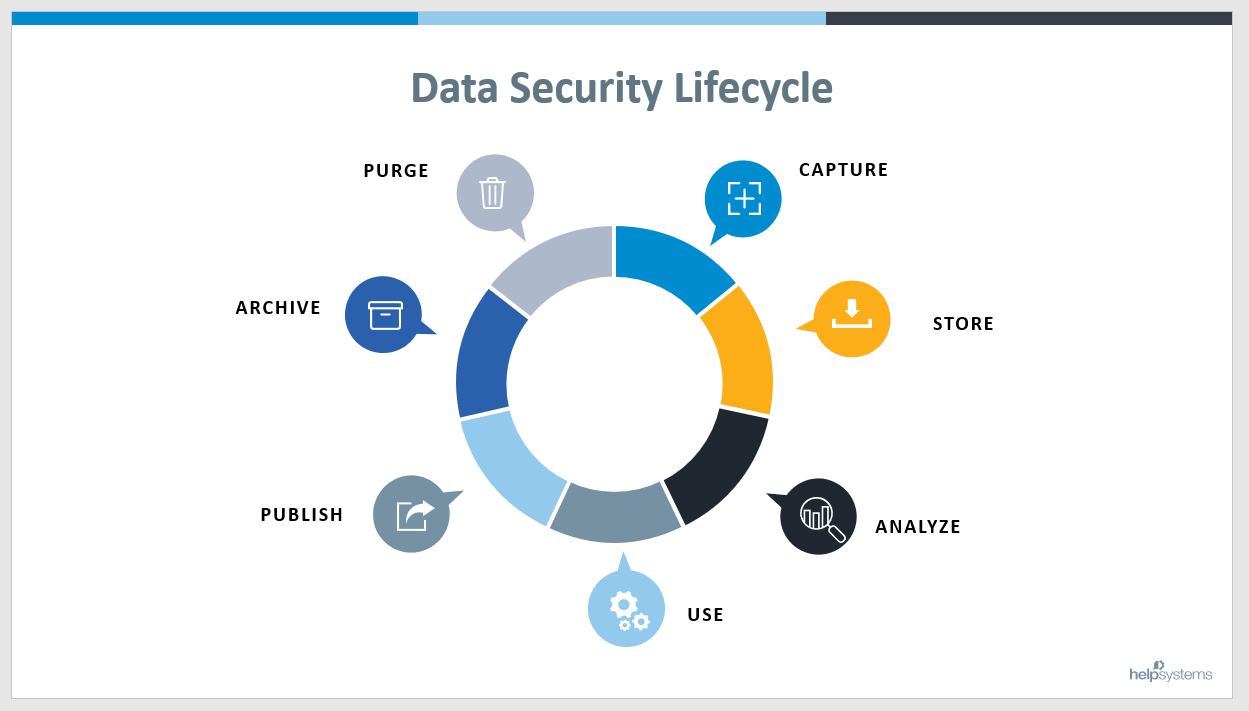
What is the Lifecycle of Data?
As you can see from the illustration below, the data lifecycle has seven distinct stages operating as a continuous, not static, process. To ensure comprehensive data security, a layer of protection should surround each stage for end-to-end security.
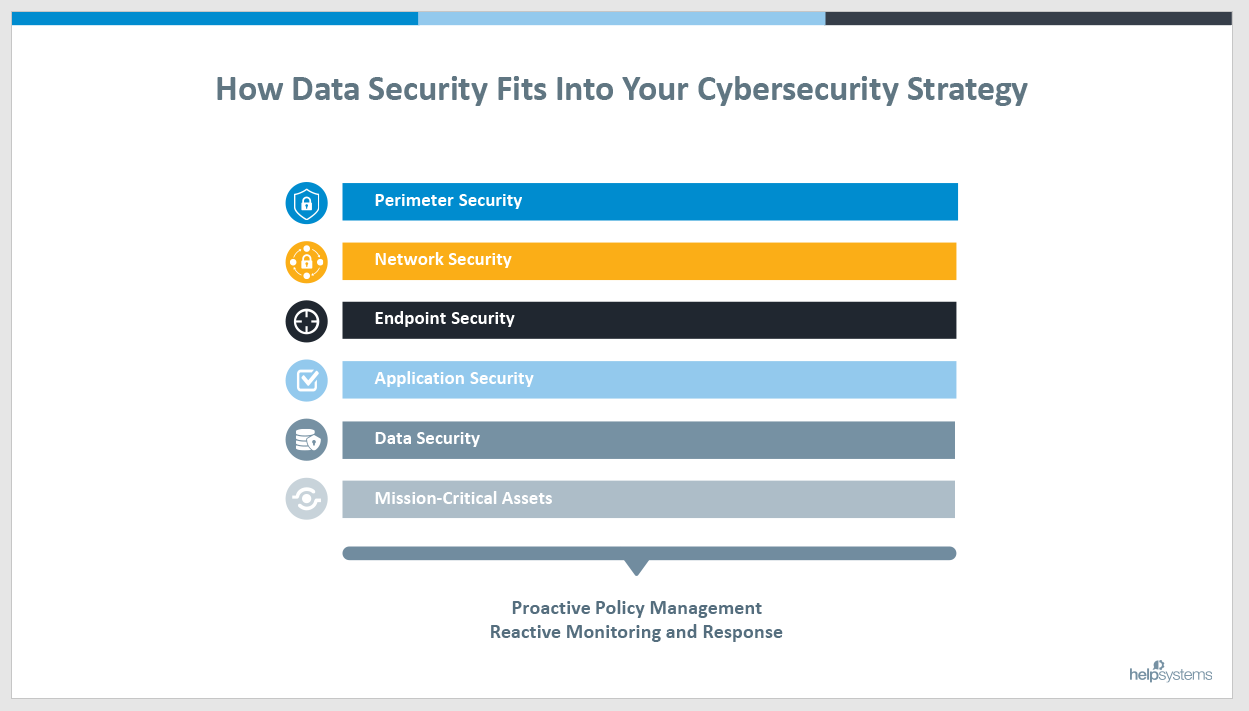
Where Does Data Fit Within Corporate Security Framework?
As you can see, data security forms the basis from which all security efforts radiate. If the data is not secure from the start, securing applications, endpoints, networks and the perimeter don’t really matter. To that end, supporting all these security measures needs to be an equal balance of proactive and reactive actions to ensure the mission-critical assets around your enterprise are safeguarded.
With data so valuable, surprising research from Verizon shows data security comprising a mere seven percent of the IT budget. Read on for details on where IT budgets could focus on for better data security.
6 Types of Data Security
Encryption
Encryption encodes data using an algorithm so it renders that data unreadable and unusable for unauthorized viewers. Regardless of whether it uses a symmetric or asymmetric key system, only those with a decryption key will be able to decipher the data.
To secure data both at rest and in motion, though, encryption may be paired with tokenization, which replaces original data with a randomly generated alphanumeric value known as a token. To retrieve the original values, an authorized user can access a token’s value in a secured token database.
A similar, yet generally more permanent form of tokenization known as data masking (or obfuscation) may also be used for data in use, where original data is hidden—or masked—by structurally similar proxy data. Data masking can be static (SDM), where data is permanently scrambled and unretrievable, or dynamic (DDM), where only authorized users can view the original data and the masked data is shown to unauthorized users.
Identity & Access Management
Identity and access management is a blanket phrase that includes all measures meant to limit digital and physical access to an organization’s critical systems and the sensitive data in those systems. Those measures often include password protection to access secured systems or databases along with authentication to confirm a user’s identity. Users should only be given the least amount of access possible to perform their job functions.
Data Backup & Leak Prevention
Data backup and leak prevention together can be thought of as preparation for a data breach, file corruption, or system failure. Regular backups should be stored on a physical disc, local network, or cloud database so as to remain available and maintain operations in the wake of such an event.
In addition to these regular backups, several tools and solutions can be implemented within an organization to further prevent a breach. These solutions can include security training for employees, the use of Managed File Transfer (MFT) for secure data movement, and Data Loss Prevention (DLP) for protection against breaches leaks, and misuse.
Activity Monitoring & Intrusion Detection
While data leak prevention addresses data loss that could happen in the future, activity monitoring and intrusion detection address insider and external threats that could be affecting your organization right now. Activity monitoring allows organizations to identify suspicious behavior and potentially prevent data loss before it occurs, while intrusion detection can help to quickly identify a breach and limit the extent of the damage.
Data Erasure
Rather than standard data wiping, organizations should prioritize more secure data erasure that overwrites data on any storage device. This ensures unauthorized users will be unable to get their hands on any sensitive information and that the data is unrecoverable.
Data Resiliency
Data resiliency refers to how well an organization can restore and maintain its systems’ availability after events like power outages and natural disasters, and directly ties in with data backups as well. Maintaining proper security even after a potentially damaging event will mean bad actors won’t be able to exploit an organization even when it’s most vulnerable.
What are the Barriers to Data Security?
Today’s organizations exchange data at a larger volume and faster pace than ever before, and they do so in complex, hybrid IT environments. In addition, the remote or partially remote workforce that emerged from the COVID-19 pandemic looks like it will be here to stay in some fashion for many enterprises for some time – increasing the points at which your data is vulnerable. Gone are the days of simply crossing fingers and hoping for the best with an emailed attachment. Today’s data transfers can be massive, complex, sent to myriad locales, and constantly at risk of interception, manipulation, and human error due to the value of that information.
This data is also subject to more stringent privacy and compliance standards designed to protect individuals as well as enterprises. Organizations that fail to secure data properly face mitigation costs that can be both financially and reputationally crippling. Human error, cybercrime, and inadequate technology all play a role in why data may be insecure. The right data security strategy, however, addresses all these factors. An organizational emphasis on data security, coupled with the robust, integrated, and complimentary software solutions, can deliver the end-to-end protection needed.
Address Data Security with a Suite of Solutions
For a state-of-the-art data security position, you’ll want to ensure your selected solutions easily integrate, work with your current IT infrastructure, and tackle the following security measures:
- Understand and classify files that may contain sensitive data
- Secure and protect sensitive data that is shared both inside and outside your organization
- Prevent, detect, and mitigate leaks of this sensitive information outside of your organization
1. Understand and Classify Your Data
The basis of a solid data security strategy begins by identifying and classifying what type of information you need to protect, including critical unstructured data such as intellectual property. By taking this step, you lock down the base control and management parameters needed to help ensure compliance.
Whether you need to protect public, financial, personally identifiable information (PII), or other types of sensitive data, establishing and classifying data to be protected sets the foundation for the additional security layers needed to continue protecting data along its journey. Our data classification solutions will protect any type of sensitive data your organization handles, follow your organization’s data security policies, and will help your organization to comply with data security laws and regulations.
2. Secure and Protect Your Data
It’s going to happen—an employee will accidentally send sensitive data to the wrong person, or perhaps transfer an otherwise “safe” document that contains hidden metadata that could compromise your compliance or privacy standards. Any number of scenarios can put your organization at risk unless you have a solution in place to detect and sanitize data in real-time before it’s sent to the cloud or to third parties and before a breach can occur.
After you’ve ensured your data is identified and classified, scrubbed of potentially sensitive data, and approved for sending by authorized users, that data now needs to be protected as it is sent or transferred for true end-to-end data security. One of the easiest ways to do so is through an MFT solution. MFT locks down your data at the point it is most vulnerable – when it is being used by others and while traveling to its destination into unmanaged domains, devices, or applications.
Securing your organization’s sensitive data throughout its entire life cycle often requires more than just its protection in transit, though. DLP solutions can help to give your organization the utmost visibility over its data no matter where it is, monitor activities and events related to that data, and create reports in the event of a compliance audit.
3. Prevent, Detect, and Mitigate Data Leaks
While implementing the right security tools like MFT and DLP are essential in preventing costly leaks, organizations need to take a holistic, top-down approach that also includes educating employees on data security risks and best practices. Making use of people-centric security awareness training is a good first step in creating the first line of defense against leaks and ideally preventing an accidental leak before one ever happens.
The threat landscape is constantly evolving and becoming more sophisticated, however, and sometimes breaches can hit even the most cautionary organizations. IT teams should operate as if a breach will occur at some point in the future, or perhaps even as if a breach is in progress right now. That’s why it’s important for organizations to prioritize identifying vulnerabilities before they’ve been exploited, detecting breaches as soon after they happen as possible, and mitigating those breaches before more damage can be done. All of this can be accomplished with solutions like Managed Detection and Response (MDR) along with data leak protection tools.
Unfortunately, even with the best security tools and response plans in place, organizations may find they lose control over their sensitive data once it leaves their corporate domain. In other words, once a breach occurs, much of the damage may already be done. But thankfully, there’s a solution for this problem as well. Digital Rights Management (DRM) tools allow organizations to have granular control over their data no matter where it goes, including the ability to adjust access controls in real-time, govern whether files are collaborative or view-only, and specify what actions can be taken with the data.
Layering data security solutions is a proactive approach to protecting your sensitive data. Read on for more details.
Related Reading: What are Data Security Solutions and How Do They Work?
Layered Security Helps Ensure Data Security
Data security is only as solid as the various elements that support it. Layering robust, proven solutions to ensure your sensitive data remains secure from start to finish is a proactive approach. Fortra's suite of data security solutions provides the range of data protection needed, including identification and classification, data loss protection, secure file transfer, and more.
Request a Fortra® Demo
From reconnaissance through achieving objectives, Fortra® interrupts attackers at every step of the attack chain.