Have you been hearing a lot about robotic process automation lately? You’re not alone—the popularity of RPA software is skyrocketing and companies of all sizes are rushing to embrace this new technology. But the speed at which RPA burst on the scene has left a lot of people feeling confused about what exactly it is and what it can do. Want to see examples of robotic process automation and learn RPA basics?
Pat Cameron, Director of Automation Technology at Fortra, recently hosted a webinar to get you up to speed on robotic process automation basics.
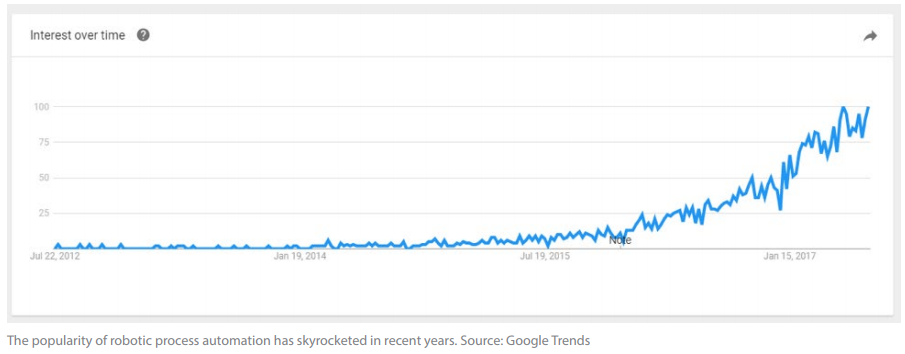
The Popularity of RPA
If it feels like the hype around robotic process automation came out of nowhere within the last few years, it’s because RPA’s popularity has been growing at an astounding rate.
According to Horses for Sources, the robotic process automation market is expected to reach $443 million in 2017—up from just $271 million the year before. By 2021, it is predicted that the market will exceed one billion.
What does this mean for you? RPA is becoming an important part of the growth strategy for companies across a wide variety of industries, and you’ll want to build your expertise on the subject to maintain a competitive edge.
In the webinar, Pat also points out that a big part of the current and predicted RPA market is services. She suggests that if you can find a robotic process automation solution that allows you to configure your automation without outside consulting, it can mean big savings for your company.
Robotic process automation may be new to your business, but key to its popularity is its ability to integrate with and streamline existing systems. For example, RPA can work together with document management or network monitoring solutions to fully automate critical business processes.
RPA Basics
One reason robotic process automation can be confusing for prospective users is that it comes along with a list of new words. For example, you may have heard people talking about a “digital workforce” or “virtual workforce” made up of “software robots.” These robots, or bots, are usually agents running on remote servers. The “digital workforce” comes in when you scale your automation so that multiple bots are being used within your organization.
If you have users running RPA processes on their desktops, the software may be referred to as a “virtual assistant” because of the way that it helps out the user with individual tedious tasks.
Comprehensive Enterprise Automation
When most people talk about automation, they’re talking about increasing productivity for individuals and teams. Robotic process automation excels in this area and many businesses and teams have saved hours just by implementing RPA for a few high-volume tasks. However, a truly enterprise-class robotic process automation solution can also go beyond the basics.
Some things to look for include robust application integrations, DevOps enablement, detailed audit reporting, cloud functionality, and infrastructure monitoring.
Creating an Automation Center of Excellence
As the word spreads about the benefits of robotic process automation, it’s tempting for businesses to deploy an RPA solution as quickly as possible. But using the technology without an underlying strategy leads to disappointing results.
First, you’ll need to put together a core team. Automation should be a company-wide project, and without someone accountable for the project, it won’t succeed. Pat recommends the team is made up of a combination of business analysts, developers, and operations staff. As you move forward, it’s critical to have evangelists or automation champions to help spread automation throughout the organization. These people will help business teams identify opportunities and see what’s possible. Finally, you’ll need executive sponsorship. Form a steering committee to help you acquire resources and gain visibility for the project.
Besides people, the other essential part of an RPA strategy is systems and infrastructure. Your technological foundation should include high availability, a disaster recovery plan, and audit capabilities. As you implement your automation, you’ll want to create some reusable templates and best practice documentation to speed along future robot configurations.
Make sure you provide adequate training to business users and the operations team. At the upper level, have dashboards available so management can have visibility into the automation project. Measure the ROI of your automated workflows to substantiate ongoing funding.
Robots in the Real World
Software robots aren’t just for the IT department, although RPA often starts in IT and spreads from there. Each department in each industry has unique tasks and workflows. Robotic process automation has the flexibility to take on any repeated process, even if it involves niche or homegrown applications.
Some industries like healthcare, insurance, and banking especially benefit from the transformative powers of RPA thanks to having high-volume processes where eliminating human error is critical.
Examples of Robotic Process Automation
In the webinar, Pat presented some real-life examples of robotic process automation in use. The first was a rental and repair company that needed to keep many manuals on file for their lists of parts. Once the manuals were scanned, an employee would have to read through the PDF, finding the parts and their descriptions and copying the information into a spreadsheet. Every time an update to a manual came out, the process had to be repeated.
Once the company implemented Automate robotic process automation, they were able to configure a robot to read through the manuals, scrape the part lists and descriptions, and enter them into the spreadsheet automatically.
Pat’s second example, from a telecom company, involved somewhat more complex workflows. When this company suffered any network problem, it would typically take them about four hours to solve. So the company implemented Intermapper, a network monitoring solution that integrates with Automate. Intermapper would discover and log network issues and open a support ticket. Next, they implemented Automate to automatically repair the issue when it arose. Repair time was reduced to less than two minutes.
To see a demonstration of Automate RPA in action, jump to 22:00 in the video. Or learn more about robotic process automation by downloading the in-depth guide to RPA.